TL;DR
- What it is: The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is an EU regulation requiring financial services firms and their ICT providers to ensure resilience against cyber threats and operational disruptions.
- Why it matters: Applies to more than 22,000 financial entities across the EU and their third-party technology partners; enforcement begins in January 2025.
- Who it applies to: Banks, insurers, investment firms, crypto service providers, cloud and SaaS vendors serving EU financial institutions.
- How Feroot helps: Feroot provides real-time visibility into client-side risks, monitors third-party scripts, and delivers audit-ready reports that align with DORA’s ICT security and risk management requirements.
Does the EU’s Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) apply to your business?
If you’re in financial services—or provide technology services to banks, insurers, or fintechs—the answer is almost certainly yes.
DORA, which takes effect in January 2025, creates a harmonized EU-wide regulatory framework to ensure that financial institutions and their vendors can withstand cyberattacks and technology disruptions. Unlike PCI DSS or HIPAA, DORA isn’t limited to payments or healthcare—it casts a wide net over operational resilience, risk management, and ICT supply chains.
For many organizations, the most overlooked DORA compliance risks live in the client-side layer of web applications. Third-party scripts, trackers, and tag managers introduce hidden vulnerabilities that threaten data confidentiality, availability, and integrity.
This is where Feroot Security comes in. Feroot goes beyond traditional compliance frameworks by providing financial entities and their vendors with the client-side observability, monitoring, and reporting capabilities they need to prove DORA compliance.
What Is DORA?
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is a regulation adopted by the European Union in January 2023. It complements the EU’s financial regulations by focusing specifically on ICT (Information and Communication Technology) risk management.
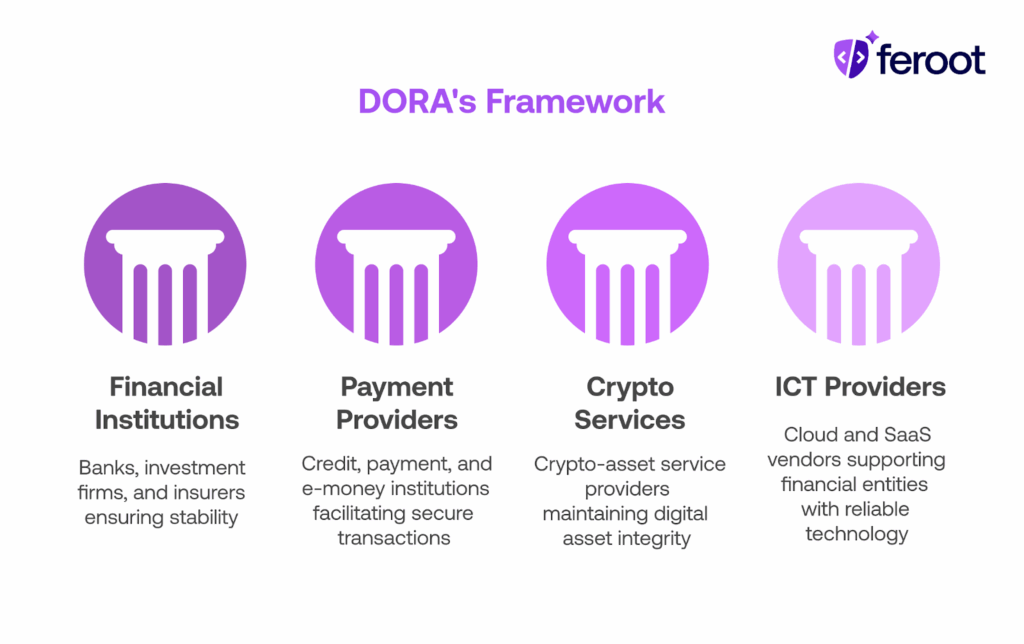
DORA applies to:
- Banks, investment firms, and insurers
- Credit institutions, payment institutions, and e-money providers
- Crypto-asset service providers
- Cloud service providers, SaaS vendors, and third-party ICT providers supporting financial entities
Its goal is simple: ensure that Europe’s financial system remains resilient in the face of cyberattacks, third-party failures, and technology disruptions.
Key Compliance Requirements
DORA sets out detailed requirements across five main areas:
- ICT Risk Management (Articles 5–14): Entities must identify, manage, and monitor risks in all ICT systems, including third-party dependencies.
- ICT-Related Incident Reporting (Articles 15–20): Firms must detect, classify, and report major incidents within strict timelines.
- Digital Operational Resilience Testing (Articles 21–24): Regular, threat-led penetration tests and vulnerability assessments are required.
- Third-Party Risk Management (Articles 25–39): Contracts with ICT providers must include risk provisions, monitoring, and auditability.
- Information Sharing (Articles 40–41): Financial entities are encouraged to exchange information on cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
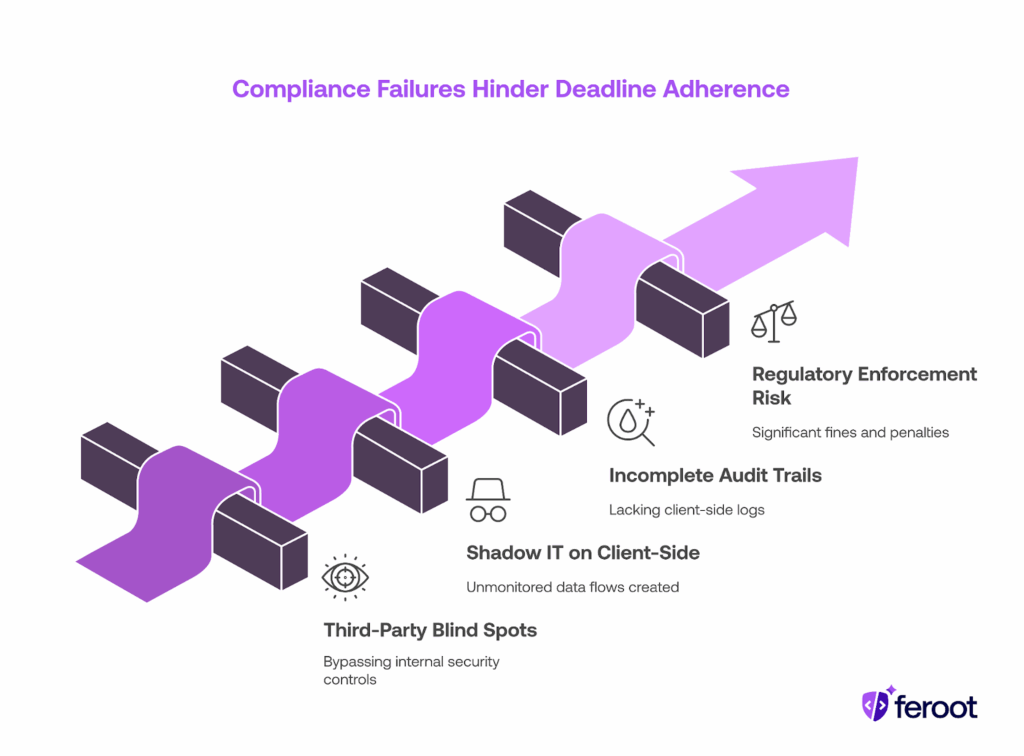
Common Compliance Failures
Despite the upcoming deadline, many organizations struggle with:
- Blind spots in third-party scripts: Marketing tags, analytics pixels, and SaaS integrations often bypass internal controls.
- Shadow IT on the client side: Business units deploy scripts without security review, creating unmonitored data flows.
- Incomplete audit trails: Regulators require verifiable evidence of monitoring and incident response, but many firms lack client-side logs.
- Regulatory enforcement risk: The European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs) can impose significant fines and penalties for noncompliance.
For example, regulators in the EU have already levied multi-million euro fines under related frameworks like GDPR for failures to secure user data. Under Digital Operational Resilience Act, similar penalties will be tied to resilience gaps and third-party risks.
How Feroot Helps with DORA Compliance
Feroot AI delivers the client-side visibility, control, and reporting financial entities and ICT vendors need to meet DORA’s requirements:
- Continuously maps and monitors all first- and third-party scripts, detecting unauthorized or malicious access that could undermine ICT resilience (Articles 5–14).
- Provides full visibility into script behavior and cross-border data flows, helping firms manage third-party risks and validate vendor compliance (Articles 25–39).
- Instantly flag unexpected script changes or injections, enabling rapid incident detection and reporting within mandated timelines (Articles 15–20).
- Generates audit-ready reports with visual proof of monitoring, aligning with regulator expectations for resilience documentation and ICT audits (Articles 21–24).
By protecting the client-side attack surface, Feroot empowers financial institutions and ICT vendors to not only achieve DORA compliance but also strengthen operational resilience across their digital ecosystems.
FAQ
What are the penalties for violating DORA?
Fines and supervisory measures vary by EU member state but can include significant financial penalties, restrictions on business activities, or withdrawal of operating licenses.
Does DORA apply to websites that use third-party trackers?
Yes. Any ICT dependency, including third-party scripts or SaaS integrations, falls under DORA’s third-party risk management provisions.
Can script monitoring help with DORA compliance?
Absolutely. Monitoring client-side scripts is critical to detecting unauthorized data access, meeting incident reporting timelines, and proving resilience.
How can I prove to auditors that my site is secure?
Feroot AI provides audit-ready reporting with logs, visual data flow maps, and evidence of continuous monitoring—meeting regulator expectations for documentation.
What tools are available to detect unauthorized third-party data collection?
Feroot AI provides real-time visibility into third-party scripts, trackers, and data flows, ensuring hidden risks are uncovered and controlled.
Conclusion
Digital Operational Resilience Act represents a major shift in how the EU regulates operational resilience and ICT risks in financial services. While many firms focus on backend controls, the client-side layer remains a critical blind spot.
Feroot Security closes that gap. By delivering real-time monitoring, script visibility, and audit-ready reporting, Feroot ensures financial institutions and their ICT vendors can meet Digital Operational Resilience Act’s stringent requirements.