TL;DR
- Iframes enable embedding of third-party content like payment forms, videos, and widgets.
- They pose serious security and compliance risks, including clickjacking, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure content delivery.
- To stay compliant—especially under PCI DSS 4.0—developers should:
- Enforce HTTPS for all iframe sources
- Set appropriate security headers (e.g., X-Frame-Options, Content-Security-Policy)
- Use the sandbox attribute to restrict iframe capabilities
- Continuously monitor iframe behavior and changes
- Feroot PaymentGuard AI automates iframe security monitoring and helps ensure ongoing PCI DSS 4.0 compliance.
Download the Free PCI 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 Checklist
Introduction
Iframes remain a vital element of modern web applications. They allow for seamless integration of third-party content such as payment forms, videos, or widgets, improving both functionality and user experience.
However, iframe use comes with potential risks. From phishing and clickjacking attacks to compliance violations under frameworks like PCI DSS 4.0, failing to secure iframe implementations can expose businesses to data breaches, fines, and reputational damage.
This article outlines the key threats associated with iframe use, best practices for securing iframes, and how to ensure continuous compliance—especially in the context of handling payment data.
Why Iframe Security and Compliance Matter
Iframes can act as silent gateways for attackers if not properly secured. Many organizations unknowingly embed third-party content without enforcing security controls, which can allow bad actors to:
- Trick users into performing malicious actions (clickjacking)
- Inject scripts that manipulate page content or steal data (XSS)
- Load insecure, non-HTTPS content that compromises data integrity
- Introduce third-party trackers or keyloggers without user consent
Regulations like PCI DSS 4.0 specifically require organizations to secure embedded components. For payment-related iframes, this includes strict control of content origins, real-time monitoring, and continuous risk assessment.
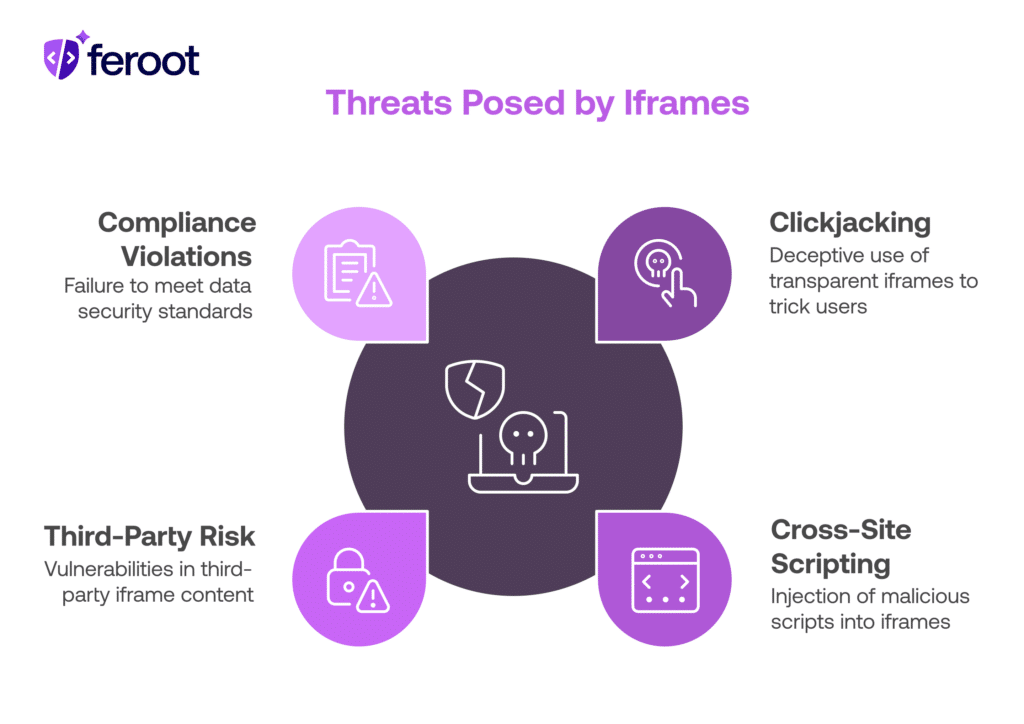
Common Iframe Threats
Clickjacking
Attackers use transparent iframes over legitimate buttons to deceive users into clicking hidden elements. This is called clickjacking can result in unauthorized purchases, data transfers, or access control violations.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Iframes can be injected with malicious scripts that run in the browser, often leveraging user sessions, credentials, or manipulating the DOM of the parent page.
Third-Party Risk
Even if your own application is secure, third-party iframe content may not be. Iframes can load tracking pixels, spyware, or vulnerable scripts that your security controls don’t detect.
Compliance Violations
Many compliance frameworks—including PCI DSS 4.0—require secure handling of customer data. Improperly configured iframes can violate requirements around secure content delivery, monitoring, and data protection.
How to Secure Iframes in 2025
Below are best practices that help mitigate iframe-related risks while meeting compliance standards.
1. Always Use HTTPS
Ensure that all iframe sources use HTTPS to prevent man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and to encrypt all communications.
<iframe src=”https://trusted.example.com/payment”></iframe>
Never embed content over HTTP. Mixed content issues will arise, and insecure sources become easy entry points for attackers.
2. Set the Correct Security Headers
Implement two critical HTTP headers:
X-Frame-Options: Prevents other domains from embedding your site via iframe. Use:
- DENY: Blocks all iframe usage
- SAMEORIGIN: Allows iframe usage only from the same domain
Content-Security-Policy (CSP): Controls which domains can embed your site or be embedded. Use the frame-ancestors directive:
Content-Security-Policy: frame-ancestors ‘self’ https://trusted.partner.com;
3. Use the sandbox Attribute
Add a sandbox attribute to iframes to restrict what the embedded content can do:
<iframe src=”https://secure.example.com/form” sandbox=”allow-forms allow-scripts”></iframe>
Without the sandbox, the embedded content may execute unrestricted JavaScript, interact with parent frames, or redirect users.
4. Validate and Whitelist All Iframe Sources
Maintain a list of approved iframe sources and restrict content loading to only those domains. This helps prevent injection of rogue content through compromised partners or outdated links.
5. Monitor and Audit Iframe Activity
Set up logging and monitoring systems that observe iframe behavior, especially in payment and authentication contexts. Detect changes such as new iframe elements, DOM manipulation, or unexpected sources.
Regular auditing ensures:
- No unapproved iframe content is introduced
- Suspicious activity (e.g., session hijacking) is detected early
- Compliance standards are continuously met
Staying Compliant with PCI DSS 4.0
PCI DSS v4.0 introduces new requirements that directly impact iframe use:
- Requirement 6.4.3: Requires scripts (including those in iframes) to be authorized and integrity-checked.
- Requirement 11.6.1: Mandates real-time alerting when script behavior changes.
For payment forms embedded via iframe, organizations must show that:
- All embedded scripts and content are explicitly approved
- Changes to those elements are monitored and trigger alerts
- Historical activity can be audited for compliance reviews
Implementing this level of oversight manually is impractical—especially at enterprise scale.
Best Practices to Maintain Compliance Over Time
Compliance is not a one-time task. To stay secure and audit-ready:
- Use CSP and X-Frame-Options consistently
- Conduct regular penetration tests on iframe-containing pages
- Keep an up-to-date inventory of all iframe sources and their risk levels
- Train developers and compliance teams on secure iframe implementation
- Create alerts for unauthorized iframe activity using behavioral baselines
Secure your Iframes with Feroot PaymentGuard AI
Feroot’s PaymentGuard AI is purpose-built to help you monitor, secure, and keep iframe elements compliant in real time.
Here’s how it helps:
- Automatic Content Monitoring: Scans for unauthorized iframe sources or scripts
- PCI DSS 4.0 Readiness: Ensures continuous alignment with 6.4.3 and 11.6.1
- Tamper Detection: Identifies when embedded elements are altered or behave unusually
- Clickjack and XSS Prevention: Uses behavioral analytics to stop iframe-based attacks
- Visual Risk Maps: Provides a clear view of where iframes are used and whether they are compliant
- AI-Powered Alerts: Instantly notifies you when iframe or script changes occur
By automating iframe oversight, PaymentGuard ensures you stay ahead of attackers and regulators—without slowing down your development cycle.
Summary Checklist: Secure Your Iframes
Use this list as your go-to guide:
- Enforce HTTPS for all iframe content
- Set X-Frame-Options and Content-Security-Policy headers
- Use the sandbox attribute for restricted functionality
- Whitelist approved sources only
- Monitor iframe behavior in real time
- Validate compliance with PCI DSS 4.0 (Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1)
- Automate with a solution like Feroot PaymentGuard AI
FAQ
What is an iframe?
An iframe is an HTML element that allows you to embed another web page within the current page. It’s commonly used for things like embedded forms, payment gateways, and videos.
Why are iframes risky?
Iframes can be exploited for clickjacking, cross-site scripting, and other attacks—especially if the embedded content is from an untrusted or unsecured source.
What are PCI DSS 4.0 iframe requirements?
PCI DSS 4.0 mandates that all scripts (including iframe-loaded ones) be approved and monitored. Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 require organizations to detect tampering and unusual behavior in real time.
How do I use the sandbox attribute?
The sandbox attribute restricts what the iframe can do. By default, it disables scripts, forms, and navigation. You can allow specific features with values like allow-scripts, allow-forms, or allow-same-origin.
Can Feroot help me pass PCI DSS compliance?
Yes. Feroot PaymentGuard AI continuously monitors iframe and script behavior, detects threats, and ensures your organization meets the necessary PCI DSS 4.0 controls—automatically.