TL;DR
- What it is: The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) gives California residents broad rights over how businesses collect, use, and share their personal data.
- Why it matters: CCPA is one of the most influential U.S. privacy laws, with ripple effects on national compliance practices and global businesses serving California consumers.
- Who it applies to: For-profit businesses that handle California resident data and meet thresholds (>$25M annual revenue, buy/sell/share data of 100K+ consumers, or earn >50% revenue from selling data).
- How Feroot helps: Feroot monitors, controls, and documents client-side scripts and trackers to help businesses prove compliance, reduce risk, and respect consumer data rights.
Does the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) apply to your online business?
If you operate a website, run targeted ads, or use third-party analytics, the answer is likely yes.
Since its enforcement began in 2020, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) has reshaped data privacy obligations in the U.S., granting California residents GDPR-like rights to access, delete, and opt out of data sales. But while companies scramble to update privacy policies and cookie banners, the client-side risks often go unaddressed.
Unmonitored JavaScript, ad tech scripts, and third-party trackers can undermine compliance by leaking consumer data without consent or opt-out controls. That’s where Feroot comes in. Beyond PCI and HIPAA, Feroot helps organizations meet CCPA obligations by providing end-to-end visibility and control over client-side data collection.
What Is the CCPA?
The California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (Cal. Civ. Code §§ 1798.100–1798.199) is California’s landmark privacy law, enforced by the California Attorney General and, since 2023, the California Privacy Protection Agency (CPPA).
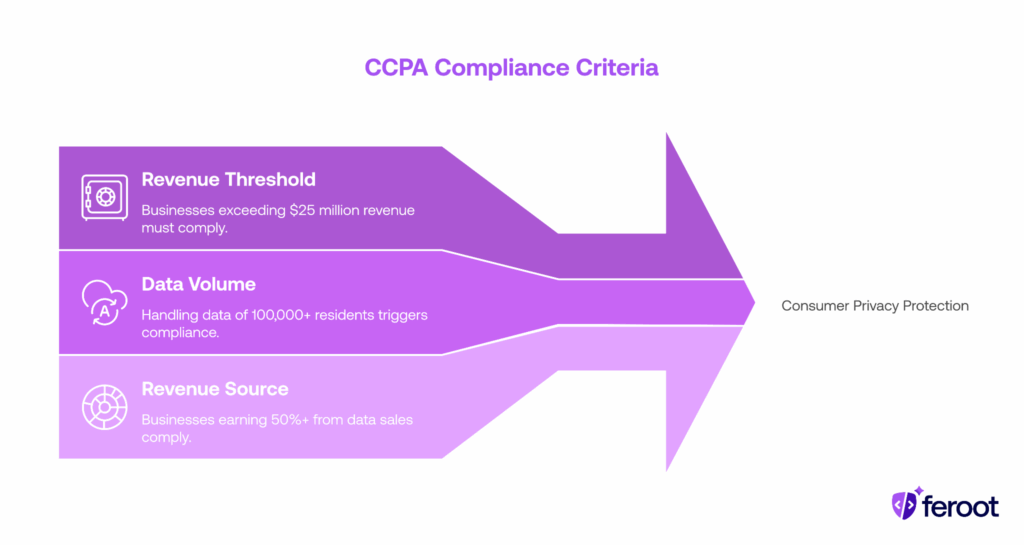
It applies to for-profit businesses that:
- Have gross revenues over $25 million;
- Buy, sell, or share personal information of 100,000+ California residents or households; or
- Derive 50%+ of annual revenue from selling consumer personal data.
CCPA covers nearly all consumer-facing industries: e-commerce, SaaS, ad tech, media, financial services, healthcare, and retail.
Key Compliance Requirements
Some of the most critical requirements under CCPA include:
- Notice at Collection (§1798.100): Inform consumers about categories of personal data collected, including via website scripts.
- Right to Know (§1798.110, §1798.115): Disclose what personal data is collected, sources, and third-party sharing.
- Right to Opt Out of Sale (§1798.120): Provide a “Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information” link and enforce opt-out choices—including across trackers and pixels.
- Right to Delete (§1798.105): Delete consumer data upon verified request, including data collected by third parties.
- Data Security (§1798.150): Implement reasonable security procedures to protect consumer data from unauthorized access, theft, or disclosure.
- Non-Discrimination (§1798.125): Cannot deny services or charge higher prices for consumers exercising privacy rights.
Common Compliance Failures
Even companies with updated privacy policies still fail CCPA audits and lawsuits because of uncontrolled client-side risks, such as:
- Dark patterns in cookie banners that don’t meaningfully enforce opt-out.
- Third-party scripts continue to transmit data (e.g., location, browsing history, identifiers) to ad tech vendors even after consumers opt out.
- High-profile cases: Sephora’s $1.2M CCPA fine (2022) for failing to disclose data sharing with ad networks and not honoring “Do Not Sell” signals from the Global Privacy Control (GPC).
These failures often stem from a lack of visibility into third-party JavaScript and trackers—a blind spot on the client side.
How Feroot Helps with CCPA Compliance
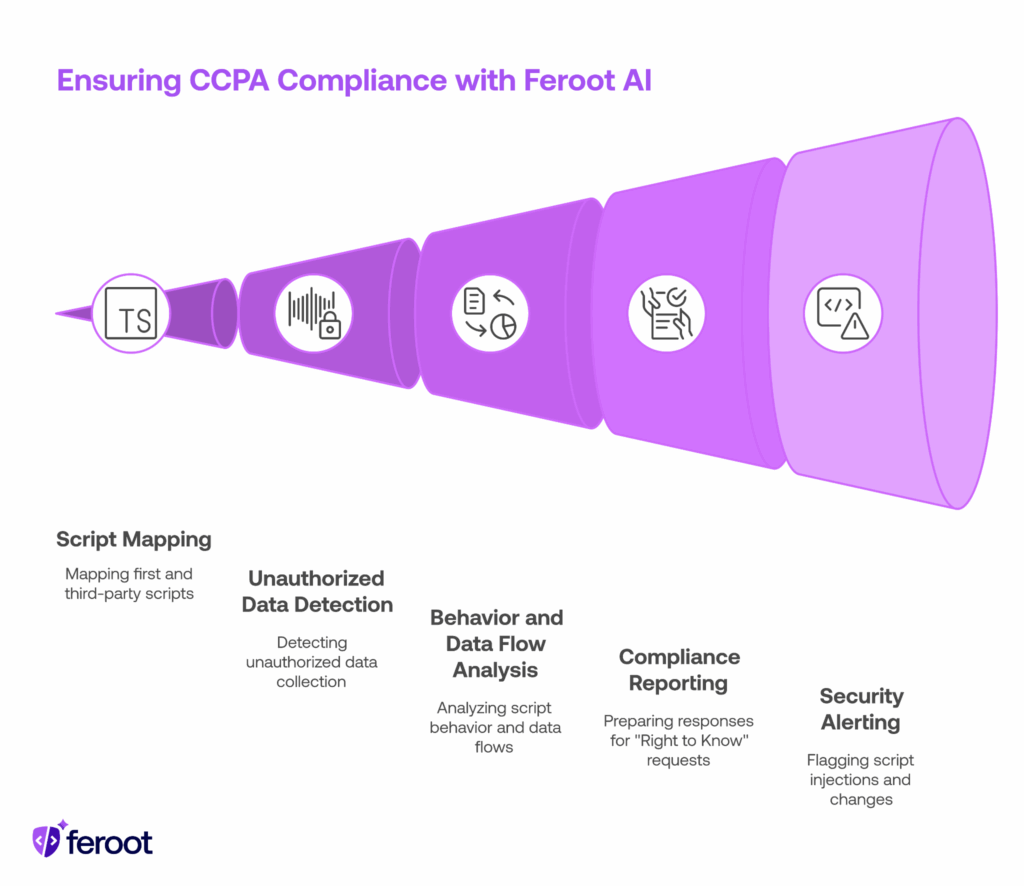
Feroot AI equips businesses with client-side security and visibility tools that directly map to CCPA’s core obligations:
- Monitors and maps all first- and third-party scripts running on web pages.
- Detects unauthorized data collection that could violate notice (§1798.100) and opt-out (§1798.120) requirements.
- Reveals script behavior and data flows, showing exactly what consumer information is being accessed, shared, or sold.
- Helps businesses prepare detailed responses for “Right to Know” requests (§1798.110).
- Immediately flags script injections, changes, or new trackers that could trigger noncompliance or data breaches (§1798.150).
- Provides visual evidence of data flows and opt-out enforcement, giving regulators proof of compliance.
By controlling hidden client-side activity, Feroot closes one of the most overlooked gaps in CCPA compliance programs.
FAQ
What are the penalties for violating CCPA?
Penalties can be up to $2,500 per violation, $7,500 for intentional violations, plus statutory damages for data breaches ($100–$750 per affected consumer).
Does CCPA apply to websites that use third-party trackers?
Yes. If those trackers collect or share California residents’ data, your business is responsible—even if the script belongs to a vendor.
Can script monitoring help with CCPA compliance?
Absolutely. Monitoring ensures opt-out choices are respected and unauthorized data sharing doesn’t occur behind the scenes.
How can I prove to auditors that my site is secure?
With Feroot’s audit logs and visual reports, businesses can show regulators exactly how scripts are monitored and data rights are enforced.
What tools are available to detect unauthorized third-party data collection?
Feroot AI continuously monitors all scripts and provides real-time alerts to protect against hidden data leakage.
Conclusion
The CCPA sets a high bar for consumer privacy in the U.S., but most compliance programs break down at the client side, where scripts and trackers operate beyond traditional IT visibility.
Feroot empowers organizations to go beyond cookie banners and policy updates by delivering real-time, client-side security and proof of compliance.


