What You’ll Learn:
TL;DR
- Why 47 new requirements change everything: PCI DSS 4.0.1 shifted from point-in-time audits to continuous monitoring, something manual checklists cannot deliver.
- What Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 actually demand: Full script inventory, authorization workflows, and real-time change detection for every payment page.
- The hidden $250K annual cost: Organizations spend on staff time, consultant fees, and audit prep, only to fall out of compliance immediately after a pass. How AI automation cuts prep time by 80%: Real-time monitoring, instant alerts, and audit-ready evidence get you into compliance without the manual scramble.
Get the 2025 PCI 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 Checklist
Why manual compliance can’t keep up
PCI DSS 4.0.1 became mandatory on March 31, 2025, bringing in 47 new requirements that fundamentally changed how compliance works. Organizations that treated PCI as an annual audit exercise now face a standard that expects real-time visibility into payment pages. Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 are the most impactful additions, which require real-time visibility into scripts and payment page changes. A spreadsheet updated quarterly can’t deliver that.
Many CISOs underestimate the actual cost of manual compliance. Beyond PCI audit fees, organizations spend hundreds of hours pulling evidence, reconciling controls, and reviewing logs. The average enterprise spends over $250,000 annually on these tasks and still risks being non-compliant the moment an attack happens. Verizon’s forensic team has documented this gap repeatedly: organizations pass audits in March and suffer breaches in April because compliance was a snapshot, not a continuous state.
The attack vectors tell the story. Magecart campaigns inject malicious scripts directly into payment pages. Third-party vendor scripts change without notification. Unauthorized modifications skim card data before encryption happens. These attacks live in the browser, where traditional perimeter defenses and manual checklists don’t look.
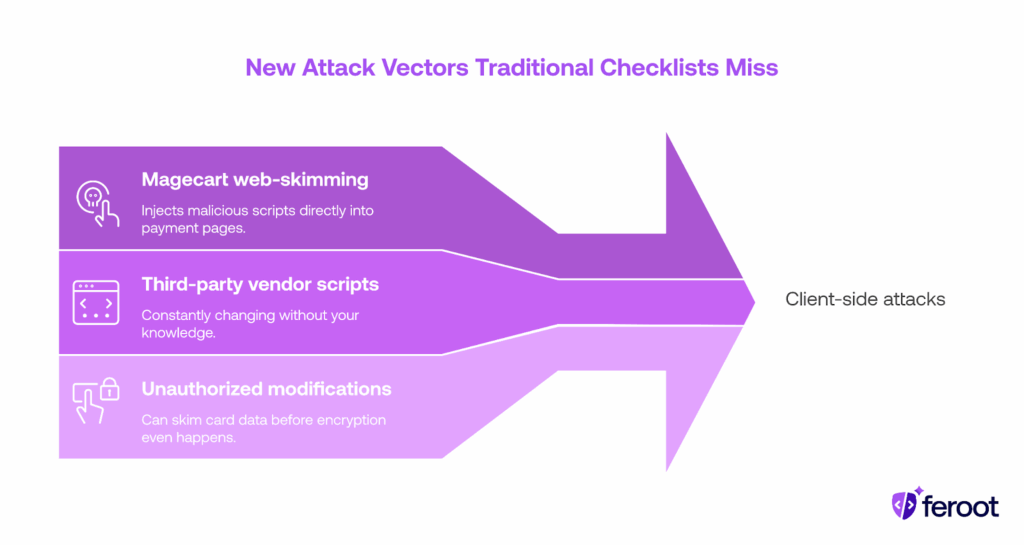
The payment page threat landscape
According to Merchant Cost Consulting, 65% of credit card fraud is now card-not-present fraud, and eight in ten currently-issued credit cards have already been compromised. The British Airways breach exemplified this perfectly. Attackers compromised a legitimate third-party library that BA’s payment pages used. The malicious code executed within the trusted browser environment. Ticketmaster suffered a similar attack through a compromised chatbot integration. The pattern is clear: approved scripts becoming malicious, legitimate vendors being compromised, trust relationships exploited.
IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report shows that the average breach in financial services costs $6.08 million. Non-compliance carries fines from $5,000 to $100,000 per month. But fines are just the beginning. Brand damage destroys customer confidence. Extended downtime halts revenue. Cyber insurance premiums spike or coverage disappears.
What changed in PCI DSS 4.0.1
The standard grew from 370 to over 500 requirements, with 47 becoming mandatory in March 2025. The requirement shifted from periodic validation to continuous monitoring. Requirement 6.4.3 demands a complete inventory of all scripts on payment pages, documented authorization for each one, and continuous verification of their integrity. Requirement 11.6.1 requires detection and alerting on unauthorized changes in real time. Not daily. Not weekly. Real-time.
These requirements directly address client-side attacks. They acknowledge that what executes in the browser matters as much as what runs on your servers. They recognize that approved scripts don’t stay trustworthy indefinitely. The old model of quarterly scans or annual audits is insufficient. Compliance today means 24/7 visibility and immediate alerting.

What continuous compliance actually looks like
The 12 core PCI DSS requirements haven’t changed, but implementation has evolved from manual reviews to automation and continuous validation.
Network security controls use real-time monitoring with instant alerts. Secure configurations rely on automated baseline monitoring that detects drift immediately. Strong cryptography means consistent Transport Layer Security enforcement plus detection of third-party scripts transmitting data insecurely. Protection from malicious software requires automated scanning for malware in JavaScript libraries.
Secure systems and software development is where PCI DSS 6.4.3 lives: maintain a complete inventory of all JavaScript on payment pages, ensure each script is authorized, and continuously verify its integrity to prevent unauthorized or malicious code.
Regular security testing is where PCI DSS 11.6.1 lives: deploy change and tamper detection that monitors payment pages (including critical HTTP headers) and alerts on unauthorized modifications, with evaluations at least weekly or on a risk-based frequency.
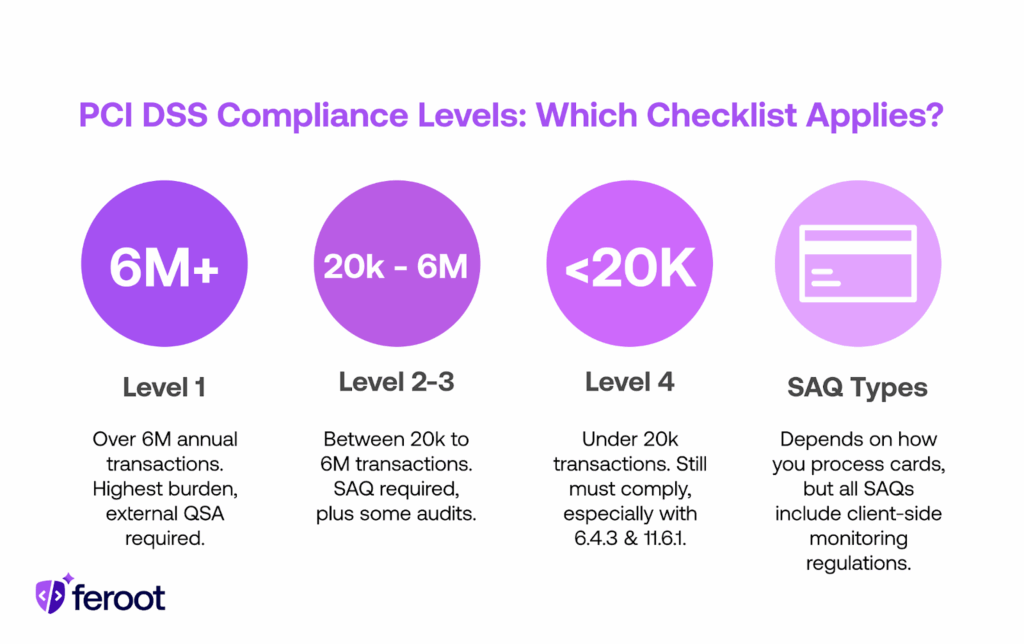
Understanding your compliance level
PCI compliance levels from 1 to 4 are based on annual transaction volume. Level 1 merchants process over 6 million transactions and face the highest burden, requiring external Qualified Security Assessor audits. Level 2 and 3 merchants process between 20,000 and 6 million transactions, requiring Self-Assessment Questionnaires (SAQs) plus some audits. Level 4 merchants process under 20,000 transactions but still must comply, especially with Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1. Your SAQ type depends on how you process cards and handle cardholder data, but all e-commerce SAQs now include client-side monitoring expectations.
The case for automation
Automated compliance works by continuously monitoring payment pages for possible violations. It provides audit-ready dashboards, instant alerts when scripts change or unauthorized modifications occur, and evidence exports that satisfy auditors without manual evidence gathering. For Requirement 6.4.3, automation maintains the script inventory automatically, validates each script against authorization records, and monitors integrity continuously. For Requirement 11.6.1, automation detects and reports unauthorized changes in real time, eliminating the detection delay that makes breaches so costly.
The ROI is measurable. Automated compliance cuts audit preparation time by 80%, eliminating weeks spent gathering evidence and reconciling logs. It reduces breach exposure by up to 70% through continuous monitoring that detects compromises in hours rather than the 197-day average Verizon documents. Organizations avoid the $250,000-plus annual cost of manual compliance tasks. IBM’s research shows that organizations with automated security save an average of $2.2 million in breach costs compared to those relying on manual processes. When a vendor pushes an emergency script update during peak sales, automated systems validate integrity against your authorization rules within seconds, eliminating the pressure to disable controls temporarily.
Working with your QSA
Many organizations view their QSA as an adversary hunting for compliance failures. This creates unnecessary friction and often results in audit outcomes that could have been avoided.
Your QSA validates that you’ve built sustainable processes, not only checking boxes at a specific period. Automating your process gives QSAs what they need: ongoing, verifiable evidence that your controls work as designed. Instead of scrambling to assemble logs and screenshots during audit season, automated monitoring preserves every script authorization, every page change, every alert in a tamper-proof trail.
This means faster assessments with fewer disputes. QSAs trust what they can verify readily. Automation ensures you can hand them that proof on demand, not just during the two weeks they’re on-site. The organizations that prepare audit-ready evidence constantly, rather than periodically, don’t just pass audits more easily. They discover possible compliance violations before auditors do, giving them time to remediate rather than explain.
The path forward
Where organizations fail most often:
- Script inventory becomes outdated within weeks: Without automation, the inventory created for audits doesn’t reflect what’s actually running in production.
- Authorization workflows turn into bottlenecks: Manual approval processes that take days cause teams to find workarounds that bypass security.
- Integrity monitoring gets disabled: False positives from poorly configured monitoring lead teams to ignore or turn off alerts entirely.
- No one owns client-side security: Payment pages fall into the gap between security teams, development teams, and marketing teams.
Start with a complete script inventory on all payment pages. Most organizations discover they’re running 30 to 60 scripts and can only document authorization for a fraction of them. Deploy real-time monitoring to establish a baseline of normal behavior and detect deviations. Prioritize Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 because they address the highest-risk attack vectors and have the steepest manual compliance costs. Treat PCI DSS as part of operational security practice, not a separate compliance exercise that happens once a year.
The continuous compliance advantage
PCI DSS 4.0.1 raised the bar significantly. With 47 new requirements now mandatory, manual processes cannot keep pace, especially with client-side risks escalating. Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 make the expectation clear: payment pages must be monitored live, scripts must be controlled in real time, and compliance must be a persistent state rather than a point-in-time achievement.
Automation turns compliance from a cost center into a security advantage. Instead of chasing annual audit deadlines, organizations gain 24/7 visibility. Instead of discovering breaches 197 days after they start, they detect unauthorized changes in real time. Instead of spending months preparing audit evidence, they export it instantly. When approached with this perspective, compliance becomes a competitive advantage rather than a regulatory burden. Start by inventorying scripts on your payment pages. Most organizations discover they’re running 30 to 60 scripts and can document authorization for fewer than half. That gap is your compliance roadmap.