TL;DR
- HHS HIPAA applies to client-side tracking: Tools like Meta Pixel and Google Analytics can expose PHI, even unintentionally, and violate HIPAA rules.
- OCR is cracking down: The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has issued clear guidance that unauthorized tracking on healthcare websites may constitute a HIPAA breach.
- Web code is a blind spot: Most security and compliance teams lack visibility into JavaScript behaviors and third-party scripts that leak PHI.
- Audit exposure is rising: Regulators are investigating tracking use without patient consent — even if no data breach is declared.
- Feroot helps fix it: Feroot’s client-side security platform detects, maps, and blocks tracking activity that could result in HIPAA violations.
Introduction
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has shared new guidance on HIPAA. This guidance focuses on using tracking technologies on public healthcare pages. This updated directive directly impacts healthcare organizations utilizing tools like Meta Pixel, Google Analytics, or session replay scripts. While these are effective for understanding user engagement, they may inadvertently collect PHI—protected health information—if configured improperly.
Regulators are making it clear that they will not take health data misuse lightly. This is especially true for HIPAA tracking technology. Additionally, officials expect HIPAA enforcement in 2025 to be even stricter, imposing hefty fines for patient privacy violations. This all underscores the urgent need for healthcare website compliance, particularly when dealing with HIPAA public web pages.
What the HHS HIPAA Guidelines Say
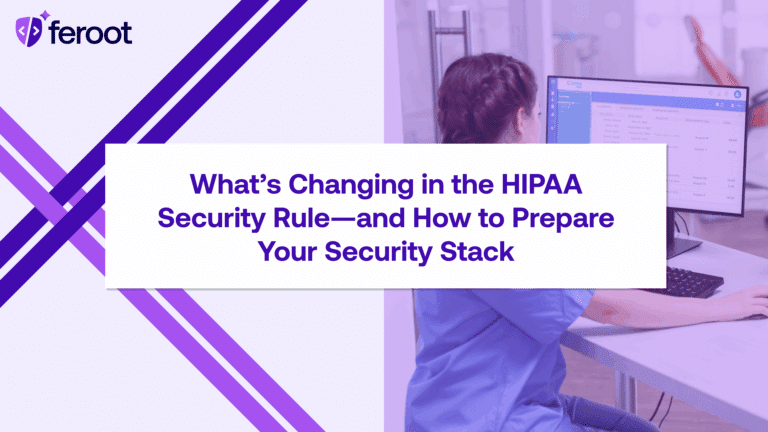
HHS follows the HIPAA law. It states that covered entities and business associates must keep electronic protected health information (ePHI) private and secure. This includes data that researchers gather from public healthcare pages. This is true even if users do not log in or use a patient portal.
Under the HIPAA privacy and security rules, organizations must protect health information that can identify individuals. This includes IP addresses, cookies, URL paths, and geolocation data when they relate to a person’s health or care.
The insurance portability and accountability rule means that organizations must protect PHI. This applies to any organization that receives, keeps, or shares PHI. They must safeguard this information, regardless of how or where they collect it.
Key Takeaways
- Public web tracking can violate HIPAA: If a healthcare site collects individually identifiable information that infers specific conditions, it’s considered PHI.
- Third-party vendors analyzing or storing PHI must sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
- Conducting a HIPAA risk assessment ensures that you account for all data flows and secure them appropriately.
Why Public Web Pages Are in Scope
Many organizations assume only patient portals or authenticated pages fall under HIPAA. However, even an open-access HIPAA compliance website can handle PHI in subtle ways, creating online PHI exposure. For example:
- A user searches for specific healthcare services like chemotherapy and lands on a page detailing cancer treatments.
- Tracking scripts then track users, collecting IP addresses or device IDs in the process.
- A webpage context such as “cancer care” can compromise patient privacy by indirectly revealing sensitive medical information.
This scenario exemplifies web tracking and HIPAA concerns. Even if a website does not ask for health details, it can still reveal someone’s health interests or conditions. This happens when the system combines user data with the webpage context. This makes third-party scripts (like analytics or marketing pixels) subject to HIPAA regulations.
Tracking Technologies Under Scrutiny
The digital compliance healthcare environment is evolving rapidly. Specific tools that raise particular concern include:
- Meta Pixel HIPAA Considerations: Meta’s retargeting pixel can collect page URLs, form data, and user identifiers. Without the right safeguards and BAAs, this can result in HIPAA breach web tracking.
- Google Analytics HIPAA risk: While widely used for web analytics healthcare, Google Analytics stores user engagement data that may tie back to a specific individual—especially when combined with other datasets.
- HIPAA cookie consent: Cookies can store session identifiers linked to sensitive content. A robust consent mechanism is crucial for data collection compliance.
Even simple scripts or plugins can accidentally record or share PHI. This shows why it is important to audit scripts on HIPAA public web pages.
HIPAA Enforcement and Risk Exposure
In 2025, HIPAA enforcement will probably be stricter about vendor compliance. They will focus on security incidents linked to web tracking and HIPAA. The Office for Civil Rights has given fines of up to $50,000 for each violation. The amount depends on how careless the actions were.
Potential consequences include:
- Financial penalties: These can escalate quickly for repeat or unaddressed violations.
- Public enforcement actions: The OCR publicizes names of non-compliant organizations, damaging reputations.
- Increased oversight: Mandatory corrective action plans, regular compliance reports, and third-party audits.
HHS has made it clear that public healthcare pages and websites can show PHI. This opens the door for more focused audits. Failing to protect PHI correctly can misrepresent the use of health data. The damage to your reputation can be worse than the fines you face.
Compliance Action Plan for Healthcare Sites
Here is a simple plan to make sure healthcare websites follow the rules and protect patient privacy:
- Website or Mobile App Audit
- Inventory all scripts, plug-ins, tags, and trackers on every page—public or private.
- Assess any embedded components on both a website or mobile app platform that could inadvertently collect PHI.
- HIPAA Risk Assessment
- Identify how your website handles online PHI exposure.
- Evaluate whether user data, page context, or third-party logs can piece together individually identifiable health information.
- Remove or Replace Non-Compliant Scripts
- If a third-party vendor cannot comply with HIPAA or sign a business associate agreement, remove their scripts.
- Explore HIPAA-focused analytics solutions that offer compliance-friendly capabilities.
- Implement HIPAA Cookie Consent
- Obtain explicit user consent for cookies that can store or transfer PHI.
- Provide clear options to opt out of trackers entirely.
- Establish Strong BAAs
- For any service that processes or stores user data from healthcare pages, you must have a legally sound BAA in place.
- This includes marketing automation platforms, analytics providers, and session replay tools.
- Ongoing Monitoring
- Track users in a responsible manner that respects their privacy.
- Deploy monitoring solutions to detect new scripts or security incidents that can lead to data leakage.
Feroot HealthData Shield AI: A Closer Look
A growing challenge in digital compliance healthcare is the sheer complexity of modern websites. Every new script or plugin can introduce a potential HIPAA breach web tracking risk. Manually reviewing each component can be time-consuming and prone to error. This is where Feroot HealthData Shield AI steps in.
Feroot HealthData Shield AI helps organizations find and lower risks on their HIPAA public web pages. The design targets covered entities and business associates.
- Automated Discovery of HIPAA Tracking Tools
- The AI checks all parts of a HIPAA compliance website. This includes hidden iframes, scripts, and cookies. It quickly flags any technologies that seem suspicious or high-risk.
- Context-Aware Analysis
- The AI can understand page content. This helps it see if a visitor’s actions show specific needs, like looking for cancer treatments. This helps detect collecting PHI in places most admins might overlook.
- Real-Time Alerts
- If someone adds a new third-party script or a plugin changes its data collection rules, Feroot HealthData Shield AI sends real-time alerts. This helps stop patient privacy violations before they get worse.
- BAA and Compliance Tracking
- For each integrated service, Feroot can log whether a valid BAA is in place, ensuring data collection compliance. It keeps track of which vendors agree to follow HIPAA privacy and security rules.
- Security Incident Reporting
- If there is suspicious behavior or unauthorized data sharing, the tool logs the event. This helps with required breach notifications under HIPAA.
By leveraging Feroot HealthData Shield AI, organizations can confidently handle web analytics healthcare, user engagement, and marketing initiatives without risking health data misuse. This proactive stance is vital to retaining patient trust and avoiding costly penalties under HIPAA enforcement 2025 guidelines.
Understanding HIPAA Fundamentals & Key Concepts
No discussion about web tracking and HIPAA is complete without mentioning important parts of the law. People know this law as the portability and accountability act. It has specific rules that are essential to understand.
- Portability and Accountability Act
- The act, often called “HIPAA,” helps people keep health insurance when changing jobs. It also protects patient data.
- HIPAA Privacy Rule
- Defines what constitutes individually identifiable health information and sets parameters for how it can be used or disclosed.
- HIPAA Security Rules
- Focus on the technical and organizational measures required to guard electronic protected health information against unauthorized access, breaches, or security incidents.
- Covered Entities and Business Associates
- Covered entities include healthcare providers, health plans, and clearinghouses. Business associates are outside organizations or people. They handle, keep, or share PHI for a covered entity.Patient Portals vs. Public-Facing Healthcare Pages
Healthcare providers have often checked patient portals for HIPAA compliance. Looking at public web pages is also important. These pages might accidentally show personal health information (PHI).
By understanding these fundamentals, organizations can more effectively craft digital compliance healthcare strategies and avoid patient privacy violations related to HIPAA tracking tools.
Best Practices for HIPAA Tracking Tools
Beyond the basic compliance checklist, there are deeper considerations to ensure your organization stays ahead of HIPAA enforcement 2025:
- Implement Zero-Trust Security Principles
- Even small websites or apps can gain from a zero-trust architecture. This approach ensures that someone carefully checks every data request or script.
- Robust Encryption
- Use TLS/SSL on all pages that handle user input. This is mandatory for any site dealing with online PHI exposure.
- Minimize Data Retention
- Limit how long you store analytics data. Less data collected means less risk of health data misuse.
- Regular Policy Reviews
- Update your privacy policy and healthcare statement often. This will help show any changes in your technology or vendor relationships.
- Secure Endpoints
- Make sure every website and mobile app endpoint is secure. This includes internal APIs that may share PHI between systems.
- User Transparency
- Make it clear how you track users, why data is collected, and how it’s protected. Transparent communication fosters trust and helps avoid patient privacy violations.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The evolving landscape of HIPAA tracking technology demands vigilance. Web tracking and HIPAA concerns are not just limited to patient portals. Public healthcare pages can also face regulatory scrutiny.
Healthcare organizations need to protect patient data. This includes managing meta pixel HIPAA settings and Google Analytics risks. They must guard against any web tracking that could lead to a HIPAA breach.
If you manage a HIPAA compliance website, a healthcare app, or both, a proactive compliance plan is key. Regular HIPAA risk assessment, thorough data collection compliance checks, and partnership with compliance-focused vendors can significantly reduce your exposure to security incidents.
Feroot HealthData Shield AI can be a key partner in this effort. It provides advanced detection and real-time protection for the many scripts and technologies that run modern healthcare websites. To prepare for HIPAA enforcement in 2025, add these solutions to your workflow. Make sure each vendor signs a business associate agreement.
Explore how Feroot Security helps healthcare organizations achieve safe, compliant, and privacy-centric digital experiences.
Follow these guidelines and OCR HIPAA guidance to maintain compliance, protect patient trust, and safeguard your organization’s reputation.
FAQs
Why are tracking pixels a HIPAA compliance risk?
Because they can collect protected health information (PHI) — including IP addresses, appointment details, and user behaviors — without consent. HIPAA requires explicit authorization before disclosing PHI to third parties.
What tools are most often in violation of HIPAA rules?
Common violators include Meta Pixel, Google Analytics, session replay tools, and other embedded trackers that transmit data to external servers without proper HIPAA-compliant agreements.
Does HIPAA apply even if we don’t store the PHI ourselves?
Yes. HIPAA governs not only storage but also transmission of PHI. If a third-party service receives PHI without proper safeguards, you may still be liable.
How can healthcare security teams detect unauthorized tracking?
You need client-side visibility — a way to monitor what JavaScript is doing in real time. Traditional server-side tools won’t catch tracking behavior that happens in the user’s browser.
How does Feroot help with HIPAA compliance for web apps?
Feroot continuously monitors and protects front-end code, detects third-party trackers, and maps activity to HIPAA security and privacy rules. It flags risky behaviors and provides audit-ready reports.