PCI DSS 4.0.1 compliance becomes manageable once you recognize that each tool protects a different layer, and the strongest programs combine them thoughtfully.
With Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 now bringing the browser into focus, organizations can finally see the complete picture they need.
What you will learn in this article
- PCI DSS 4.0.1 Requirements 6.4.3/11.6.1 are now enforceable and specifically require client-side monitoring of payment-page scripts, as traditional tools don’t cover this.
- Feroot PaymentGuard AI is the purpose-built control for the browser layer. Pair it with GRC and security tools to cover the rest.
- Map each tool to its true surface and evidence, and you’ll have a stack that protects customers and passes audits without gaps or overlap.
Understanding PCI compliance ecosystem
When teams begin mapping their path to PCI DSS 4.0.1 compliance, one pattern quickly emerges: there’s no single tool that does it all.
Drata handles governance. Qualys scans your infrastructure. Invicti tests your apps. Akamai defends the edge. HUMAN Security stops bots. Yet none reach the browser, where many attacks now begin.
Most teams still juggle 4–6 specialized tools to get full coverage.
That gap became a formal requirement on March 31, 2025, when PCI DSS 6.4.3 and 11.6.1 took effect.
These controls demand real-time authorization, integrity validation, and tamper detection of client-side scripts, an area where Feroot PaymentGuard AI is purpose-built.
What we see teams do successfully is integrate these layers into the most resilient compliance programs rather than choosing between them.
This comparison clarifies how each tool fits together, enabling organizations to achieve complete, layered PCI compliance without overlap or gaps.
Quick comparison overview
| Tool | Category | Primary Focus | Key PCI DSS Requirements | Complements PaymentGuard AI? |
| Feroot PaymentGuard AI | Client-Side Security | Browser script monitoring | 6.4.3, 11.6.1 | Core capability |
| Drata | GRC Automation | Evidence collection, policy management | 12.x, 10.x (documentation) | Yes – Collects evidence from PaymentGuard AI |
| Qualys VMDR | Vulnerability Scanning | Infrastructure scanning | 11.3.2 (external ASV scans), 11.3.1 (internal vulnerability scans) | Yes – Different attack surface |
| Invicti | Application Security | DAST/IAST testing | Requirement 6 (secure software lifecycle; application vulnerability testing). | Yes – Tests your code vs third-party code |
| Scrut | GRC Automation | Compliance management, risk scoring | 12.x, 10.x (documentation) | Yes – Documents PaymentGuard AI monitoring |
| Akamai | Edge Security | CDN, WAF, DDoS protection | 1.2.1, 6.6.1, 4.2.1 | Yes – Different security layer |
| HUMAN Security | Bot Detection | Fraud prevention, bot mitigation | Supports 8.x, 10.x (fraud) | Yes – Different threat vector |
The critical gap: Why client-side security requires a dedicated solution
Client-side code runs directly in the user’s browser, where attackers can access, modify, or inject malicious scripts without touching the server. This exposure is exactly why PCI DSS 6.4.3 and 11.6.1, now in effect and enforceable, require continuous client-side monitoring.
Traditional tools can’t meet these controls because:
- They don’t monitor browser-executed JavaScript
- Infrastructure scanners assess servers
- Application testing tools validate code
- SIEMs collect logs, and WAFs secure the network edge
Yet none observe the behavior of third-party scripts running in users’ browsers where analytics tags, chatbots, CDNs, and payment widgets operate. Achieving compliance now requires dedicated client-side monitoring, which is precisely what PaymentGuard AI was built to provide.
PaymentGuard AI: Purpose-Built for Requirements 6.4.3 & 11.6.1
Among PCI DSS 4.0.1 solutions, Feroot PaymentGuard AI stands apart for addressing one of the hardest-to-meet mandates: client-side security. It’s explicitly designed for Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1, which require organizations to monitor, validate, and detect unauthorized changes in scripts running within the user’s browser.
While tools like scanners, WAFs, and SIEMs monitor networks and servers, they cannot see JavaScript execution at runtime. PaymentGuard AI fills that gap. It continuously inventories and monitors every third-party script, validates integrity, detects Magecart-style tampering, and produces QSA-ready compliance evidence. It’s the purpose-built solution for any website with third-party scripts on payment pages.
PaymentGuard AI vs GRC Automation (Drata & Scrut)
Drata and Scrut focus on automating the governance and documentation side of PCI DSS compliance. Drata offers pre-mapped PCI DSS controls, 75+ integrations, and multi-framework alignment.
Scrut provides a more affordable GRC platform with risk scoring, automated testing, and auditor collaboration features. Both simplify policy management and continuous control monitoring.
What PaymentGuard AI does differently
Feroot PaymentGuard AI is designed for the technical enforcement of PCI DSS Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1, which are the controls that mandate real-time monitoring of scripts executing in the browser. While GRC platforms manage compliance documentation, PaymentGuard AI delivers the actual evidence, like continuous script inventory, integrity validation, and detection of unauthorized changes.
In practice, organizations use both. PaymentGuard AI provides the real-time monitoring data for client-side compliance, while Drata or Scrut aggregates that data into audit-ready reports.
PaymentGuard AI vs Infrastructure Scanning (Qualys)
Qualys is an ASV-certified vulnerability management platform trusted for its infrastructure-level scanning. It performs quarterly external and authenticated internal scans, identifies missing patches, and helps support PCI DSS Requirements 11.3.1, 11.3.2, and 6.3.3.
What PaymentGuard AI does differently
Feroot PaymentGuard AI addresses an entirely different layer, which is the client side. While Qualys looks for vulnerabilities on servers and networks, PaymentGuard AI continuously monitors JavaScript executing in browsers and fulfills PCI DSS Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1.
You need both as mandated by PCI DSS 4.0.1. Qualys ensures your infrastructure is secure, while PaymentGuard AI ensures the checkout experience in the browser remains uncompromised.
PaymentGuard AI vs Application Security Testing (Invicti)
Invicti focuses on application-layer security through Dynamic and Interactive Application Security Testing (DAST/IAST). It scans web applications to uncover vulnerabilities like XSS, SQL injection, and insecure configurations before they reach production. It mainly supports PCI DSS Requirements 6.4.2 and 6.5.1.
What PaymentGuard AI does differently
While Invicti tests the code you write, Feroot PaymentGuard AI monitors the code others write, the third-party scripts executing in browsers after deployment. It continuously validates script integrity, detects unauthorized modifications, and directly aligns with PCI DSS Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1.
You need both because a modern checkout flow involves both first-party code and third-party JavaScript. Invicti secures your source code before release, while PaymentGuard AI protects the runtime environment.
PaymentGuard AI vs Edge Security (Akamai)
Akamai safeguards the network edge with one of the world’s largest content delivery and security platforms. It provides CDN optimization, WAF protection, DDoS mitigation, and API security, supports Requirements 1/4/6 depending on deployment.
What PaymentGuard AI does differently
Feroot PaymentGuard AI starts where Akamai ends, within the browser. It monitors the JavaScript that executes after the page is delivered, detecting unauthorized changes, digital skimming, and data exfiltration that occur beyond Akamai’s visibility.
You need both because Akamai protects the content before it reaches your servers. PaymentGuard AI monitors after it reaches your users’ browsers. Together, they close the loop covering two essential but distinct layers of PCI DSS compliance.
PaymentGuard AI vs Bot Detection (HUMAN Security)
Human Defense Platform verifies over 20 trillion digital interactions weekly using AI and behavioral analytics to stop malicious automation at speed and scale. It supports PCI DSS indirectly through Requirements 8.x and 10.x, which cover access control and fraud prevention.
What PaymentGuard AI does differently
While HUMAN fights automated attackers, Feroot PaymentGuard AI defends against malicious scripts running in users’ browsers. It detects compromised third-party code, prevents data skimming, and ensures script integrity on payment pages.
Bot detection and client-side monitoring address different, complementary threats: HUMAN stops fraud before it begins, while PaymentGuard AI protects customer data once the page loads
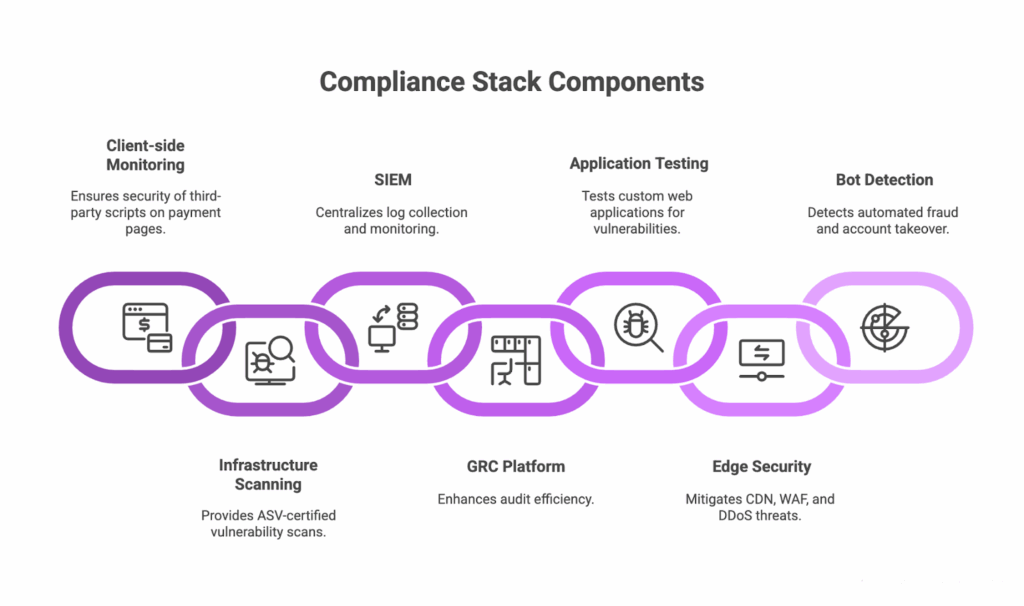
How to Build Your Complete Compliance Stack
What we’ve learned from mature programs is that PCI DSS 4.0.1 compliance comes from thoughtfully combining specialized tools, each protecting a different layer of your environment. No single platform can do it all.
The stack that works for you depends on your specific situation. Your environment size, payment flow complexity, and existing controls all shape what you actually need. Smaller teams often succeed by starting with three essential layers: client-side monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and GRC automation. As your compliance scope grows, you add specialized tools where they make sense rather than buying everything upfront.
- Client-side monitoring (PaymentGuard AI): Required if any third-party scripts run on payment pages; fulfills PCI DSS 6.4.3 & 11.6.1.
- Infrastructure scanning (Qualys): Required for ASV-certified vulnerability scans.
- SIEM (Splunk or ELK): Required for centralized log collection, monitoring, and retention.
- GRC platform (Drata or Scrut): Highly recommended for improving audit efficiency.
- Application testing (Invicti): Essential for custom web applications.
- Edge security (Akamai): Critical for CDN, WAF, and DDoS mitigation.
- Bot detection (HUMAN Security): Important for detecting automated fraud, credential stuffing, and account takeover.
Quick decision guide
Based on engagements with peer organizations, teams achieve the strongest PCI DSS 4.0.1 results when they build a compliance stack designed for collaboration, not consolidation. Each tool plays a defined role.
The framework below offers a practical way to determine which tools align best with your environment.
| Tool / Platform | You Need It If |
|---|---|
| PaymentGuard AI |
☐ Your payment pages use third-party scripts (analytics, chatbots, CDNs, widgets)
☐ You need visibility into browser-executed code
|
| GRC Platform (Drata / Scrut) |
☐ You manage or plan to pursue multiple compliance frameworks (SOC 2, ISO 27001, PCI DSS, etc.)
☐ You want automated evidence collection and audit readiness
|
| Qualys |
☐ You perform quarterly ASV scans for internet-facing systems
☐ You manage infrastructure that needs vulnerability assessment
|
| Invicti |
☐ You build or maintain custom web applications
☐ You need dynamic and interactive testing for security vulnerabilities
|
| Akamai |
☐ You require CDN performance optimization and DDoS protection
☐ You want edge-level WAF protection before traffic reaches servers
|
| HUMAN Security |
☐ You face bot-driven fraud, fake account creation, or carding attacks
☐ You need credential stuffing and account takeover defense
|
PaymentGuard AI in your PCI stack
In our experience, PCI programs stall when the browser is treated as a black box. PaymentGuard AI is the purpose-built solution for PCI DSS 4.0.1 Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1, which became mandatory and enforceable on March 31, 2025.
Pair it with infrastructure scanning, GRC automation, application testing, edge security, and bot defense, and you have a stack that protects customers and stands up to audits.
Ready to address PCI DSS Requirements 6.4.3 and 11.6.1? Schedule PaymentGuard AI Demo.
How quickly can I deploy Feroot PaymentGuard AI?
Most customers are monitoring production payment pages within 24 hours. Deployment involves adding a lightweight JavaScript tag, no infrastructure changes required. Feroot’s “set and forget” approach means the AI immediately begins learning approved script behavior, and you can enable automated blocking within 24 to 48 hours. Minimal ongoing maintenance required after initial setup.
Which tools are mandatory vs optional?
Mandatory for most: client-side monitoring when third-party scripts touch payment pages, quarterly ASV scans for internet-facing systems, and a SIEM for log management.
Highly recommended: a GRC platform, application testing if you ship custom code, and edge security or DDoS protection as your exposure grows.
How do these tools integrate?
Technical controls (PaymentGuard AI, Qualys, Invicti, Akamai, HUMAN) send alerts and logs to your SIEM. Your GRC platform collects evidence from those systems for auditors. That pattern gives operations a real-time signal and audit teams clean documentation.
What happens if we don’t address Requirements 6.4.3 & 11.6.1?
These became mandatory on March 31, 2025. If payment pages load third-party scripts and you lack client-side monitoring, passing a PCI DSS 4.0.1 assessment is unlikely.
Related reading
- What is the Best PCI DSS Compliance Software for 6.4.3 and 11.6.1?
- Cloudflare vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- HUMAN Security vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Qualys vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Invicti vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Imperva vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Akamai vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Drata vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Scrut vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Sprinto vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- RiskWatch vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Hyperproof vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Tenable Nessus vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Vanta vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI
- Datadog vs Feroot PaymentGuard AI