Introduction
In 2025, cyber threats are evolving faster than ever—and so must your approach to data breach prevention. With the average cost of a breach now exceeding $4.5 million, organizations need more than antivirus software and firewalls. They need proactive, layered strategies that encompass technology, people, and policy.
This guide delivers a comprehensive look at modern data breach prevention strategies, helping organizations minimize exposure, maintain compliance, and build cyber resilience in an ever-shifting threat landscape.
Why Data Breach Prevention Still Matters in 2025
Data breach prevention isn’t just a technical concern—it’s a business-critical priority. In 2024 alone, organizations across industries suffered over 2,200 verified breaches. From credential stuffing and ransomware to insider threats and third-party compromise, attackers have expanded their tactics.
Factors that make data breach prevention vital in 2025 include:
- Remote and hybrid work: Increased endpoints and access points.
- Cloud reliance: Misconfigurations in cloud environments are now a top cause of breaches.
- Compliance obligations: GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS demand demonstrable security.
- Brand reputation: Data loss erodes customer trust and impacts revenue.
Effective data breach prevention is not just about avoiding financial loss—it’s about preserving your business’s operational integrity and public image.
Core Elements of a Data Breach Prevention Strategy
A strong data breach prevention strategy should include the following foundational components:
- Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): Assume no device or user is trusted. ZTA requires verification at every step, enforcing strict identity and access controls.
- Risk Assessments: Routine assessments help identify new vulnerabilities as systems evolve. Document your risk register and address gaps in priority order.
- Access Management: Implement least privilege access, where users only get the data access they need. Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and privileged access management (PAM) tools.
- Encryption and Data Minimization: Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit. Avoid over-collecting or storing data longer than necessary—both reduce breach impact.
- Security by Design: Build cybersecurity into systems from day one. Avoid bolting on solutions after launch.
Best Practices for Mitigating Risk
Data breach prevention is an ongoing process. Organizations must adopt a multi-layered defense strategy using proven best practices:
- Patch management: Regularly update software, firmware, and plugins to close known vulnerabilities.
- Segmentation: Isolate networks to prevent lateral movement during a breach.
- DLP Solutions: Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools monitor and block unauthorized data transfers.
- Vendor Vetting: Third-party vendors can introduce hidden risk. Ensure all partners meet your security standards.
- Logging & Auditing: Maintain immutable logs for every access and change. These are critical during investigations.
Each of these practices directly contributes to reducing breach surfaces and increasing visibility across the infrastructure.
Modern Tools & Technologies to Deploy
Your data breach prevention strategy should leverage advanced tools to monitor, detect, and block malicious activity:
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): Correlates telemetry across endpoints, servers, and cloud.
- SIEM Platforms: Centralize and analyze logs for threat detection.
- CASBs (Cloud Access Security Brokers): Enforce security policies across SaaS and cloud applications.
- Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR): Monitors user behavior to flag anomalies in real time.
By integrating these tools into your architecture, your business strengthens its ability to stop breaches before damage occurs.
The Human Factor: Training and Policies
Even the most advanced technology cannot protect against human error without proper training. In fact, 88% of breaches involve some level of employee mistake.
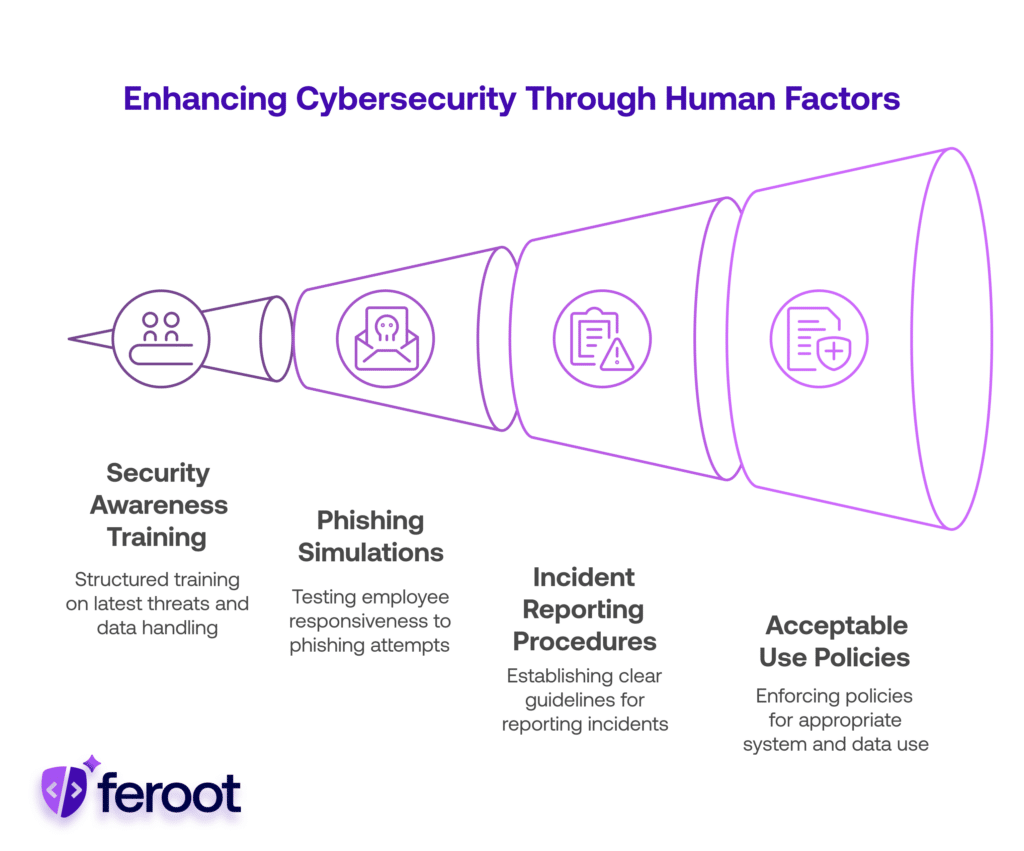
Employee-Focused Data Breach Prevention Measures:
- Annual security awareness training: All employees should undergo regular, structured training that covers the latest threats and safe handling of sensitive data. This reinforces a culture of cybersecurity and ensures staff can recognize and respond to emerging risks.
- Phishing simulations to test responsiveness: Simulated phishing campaigns help gauge how employees react to deceptive emails and links in a controlled environment. These exercises allow businesses to identify vulnerable users and tailor follow-up education accordingly.
- Clear incident reporting procedures: Employees must know exactly how and when to report suspicious activity, potential breaches, or lost devices. A well-defined process reduces delays in response time and minimizes potential damage during a security incident.
- Acceptable use policies (AUPs): AUPs outline the appropriate use of company systems, data, and internet access to prevent negligent behavior. Enforcing these policies through regular reminders and acknowledgment forms strengthens compliance and accountability.
Ensure that executives, staff, and contractors understand the importance of protecting sensitive information—and are held accountable.
Proactive Monitoring and Incident Response
Prevention doesn’t eliminate the possibility of a breach. That’s why a robust incident response (IR) plan is a cornerstone of data breach prevention.
Key IR practices:
- Develop a response playbook: Include checklists for detection, containment, notification, and recovery.
- Run tabletop exercises: Test your team’s readiness before real-world attacks occur.
- Automate where possible: Use tools for real-time alerts, containment actions, and forensic analysis.
Monitoring should be continuous. Threats evolve hourly—your defenses must as well.
Integrating Feroot’s Client-Side Security
One often-overlooked area in data breach prevention is the client-side—especially in web applications. JavaScript vulnerabilities, malicious third-party scripts, and formjacking attacks are common blind spots.
Feroot Security helps secure your website’s front-end by providing:
- Visual script mapping to detect unauthorized changes
- Real-time monitoring of DOM-based activity
- Compliance assurance for standards like PCI DSS and HIPAA.
By integrating Feroot’s PaymentGuard AI and HealthData Shield AI, organizations can block unwanted scripts and ensure that customer data—especially health or financial information—is never exposed at the browser level.
Conclusion
Data breach prevention in 2025 is no longer about firewalls alone—it’s about a comprehensive, evolving, and layered defense that aligns with both technology and human behavior. Organizations must anticipate risk, not just react to it.
Key Takeaways:
- Build security into architecture early using zero trust principles.
- Use tools like XDR, EDR, and DLP to detect and contain threats.
- Train every employee to be a security asset, not a liability.
- Monitor client-side scripts with tools like Feroot to close hidden gaps.
- Regularly test and refine your incident response plans.
Proactive data breach prevention isn’t a one-time initiative—it’s an ongoing commitment. Businesses that continuously adapt to the evolving threat landscape will be better positioned to maintain trust, avoid regulatory penalties, and stay ahead of malicious actors.


